Magnesium is an essential mineral that serves over 300 vital functions in the human body. It plays critical roles in energy production, blood sugar regulation, and muscle and nerve function, making it critical for overall health and well-being. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for magnesium is 310-320 mg daily for non-pregnant adult women.
Nutrient needs increase substantially during pregnancy for multiple nutrients to support rapid growth and development. Pregnant mothers require significantly higher amounts of nutrients like choline, iron, folate, and magnesium to nourish themselves and their growing baby. All of these, including magnesium, are essential nutrients. This means we must consume them through food and sometimes supplements to meet our needs.
Magnesium plays a role in bone formation, blood pressure regulation, and thyroid function. These systems and functions are essential during the nine months of gestation. Naturally, maintaining adequate magnesium levels through diet and supplementation is highly recommended as a priority. Studies have linked magnesium deficiency in pregnancy to conditions and symptoms like preeclampsia, preterm birth, and low birth weight.
Ideally, your diet and prenatal vitamin combination will include enough magnesium to meet your daily requirements. However, not all prenatal vitamins include magnesium. Check your supplement facts label to determine if your prenatal vitamin has magnesium. (Here are some tips on what to look for in prenatal vitamins! For our full guide and recommendations, join The Prenatal Nutrition Library.)
Given magnesium’s evident importance for moms’ and babies’ wellness, I will share an informative roundup of the many benefits expectant mothers can gain by optimizing their magnesium intake.

10 Benefits Of Magnesium During Pregnancy
Reduces Leg Cramps
Magnesium helps to relax muscles and regulates muscle contractions. This unique function helps to reduce uncomfortable leg cramps that are the bane of existence for many pregnant women. Magnesium deficiencies can be a sneaky cause of leg cramps in pregnant women.
Pregnant people need between 350 to 400 milligrams of magnesium daily, depending on age. Prioritize, including plenty of magnesium-rich foods in your diet. If that doesn’t work, talk with your dietitian about magnesium glycinate supplementation to help alleviate these cramps.
May Lower the Risk of Preterm Birth
A randomized control trial concluded that magnesium supplementation during pregnancy may lower the risk of preterm birth. Magnesium sulfate is also commonly administered to pregnant women at risk of preterm labor to help stop contractions.
Supports Healthy Birth Weight
Studies show magnesium levels are associated with birth weight. Babies born to mothers with low magnesium levels may be at increased risk for low birth weight. Optimizing magnesium intake through diet and supplementation may help support appropriate fetal growth and weight.
May Help Curb Morning Sickness
Morning sickness can be overwhelming during pregnancy. Nausea, vomiting, aversions, and fatigue often plague the first trimester of pregnancy. There are many factors and possible contributors to morning sickness. We still don’t fully know the cause of this super common pregnancy symptom. Magnesium will likely not “cure” morning sickness, but it could reduce symptoms’ severity. So, increasing your magnesium intake is a win-win!
Supports Healthy Blood Pressure
Magnesium plays a role in regulating blood pressure levels. In turn, its deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of preeclampsia and high blood pressure during pregnancy. Maintaining proper magnesium levels through supplementation (if needed) can help support healthy blood pressure levels and may play a role in preventing pregnancy complications like preeclampsia.
Helps Fights Fatigue
Magnesium plays a crucial role in energy production and metabolism. Low magnesium levels contribute to the common symptom of fatigue experienced during pregnancy. Consuming adequate amounts of magnesium-rich foods like pumpkin seeds, almonds, and avocado can help to support energy levels during pregnancy.
Supports Overall Fetal Development
Magnesium is involved in many cellular functions and protein synthesis during pregnancy. It plays a role in a baby’s bone, teeth, and neural development. Increasing magnesium intake through diet and supplementation, if needed, supports overall fetal growth and development.

Plays a Role in Reducing the Risk of Gestational Diabetes
A few studies have found a link between low magnesium levels during pregnancy and the development of gestational diabetes. Magnesium plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels. By ensuring enough magnesium in your diet, you’re giving yourself a head start towards reducing the risk for gestational diabetes.
May Reduce the Risk of Postpartum Depression
Magnesium has been linked to the psychological and mental health of women during pregnancy. There is much to learn in research, but it may play a role in the prevention and risk reduction of postpartum depression, which impacts many women in the days, months, and weeks after delivery.
Ensuring proper magnesium levels through diet and supplementation (when needed) during pregnancy and after may help support maternal mental health and wellness.
Supports Improved Mood During Pregnancy
Magnesium plays a crucial role in neurotransmitter regulation and production. Neurotransmitters, like serotonin, play a key role in promoting good mood. Low magnesium levels have been associated with symptoms of depression and anxiety in pregnant women.
Consuming enough magnesium through foods like pumpkin seeds, almonds, and avocado or magnesium supplementation when needed can support and promote a brighter mood during pregnancy.

Best Foods With Magnesium For Pregnancy
Spinach
This leafy green is a magnesium-rich vegetable containing just over 150 mg of magnesium in one cup of cooked spinach. Cooked spinach is an excellent source of magnesium and also delivers vitamin K, folate, some non-heme iron, and antioxidants that support maternal health and fetal development. Spinach is a highly recommended food for every person during pregnancy if they enjoy it!
While raw and cooked spinach can be incorporated into a healthy diet for pregnancy, cooked spinach contains significantly more magnesium per cup. One cup of raw spinach has about 24 mg of magnesium. Be sure to thoroughly wash raw spinach before consuming.
Almonds
Almonds are an excellent food for pregnant women. They’re a good source of non-dairy calcium, boost fiber, and contain healthy monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. All of these nutrients support a healthy pregnancy. Almonds may even help curb morning sickness and provide protein when dealing with meat aversions!
Almonds are a nutritious snack option during pregnancy as they satisfy hunger and help support your energy levels when consumed in moderation. One ounce of almonds, or about 23 whole almonds, offers 76 mg of magnesium. Consuming nuts, like almonds, that have been soaked and then roasted versus raw can help aid digestibility. Practice moderation with almonds to avoid an upset stomach.
Add almonds to a homemade snack mix or spread some almond butter on a slice of whole-grain or sourdough toast.
Pumpkin Seeds
These crunchy super-seeds harbor about 75 mg of magnesium in a 1⁄4 cup serving. It only takes a handful of pumpkin seeds to boost your magnesium intake. They supply a unique combination of various nutrients, including non-heme iron, zinc, plant-based omega-3 fatty acids (ALA), vitamin A, protein, and fiber that nourish you throughout gestation. Pumpkin seeds are also called pepitas.
There are different ways to enjoy pumpkin seeds. Lightly roasting them in an oven before spreading them over a salad or eating them as a snack is a great option. This enhances their taste and flavor. You can also buy pepitas to sprinkle over yogurt bowls or salads. For more healthy pregnancy snack ideas, check HERE.
Avocado
One-half of avocado delivers nearly 60 mg of magnesium, heart-healthy fats, fiber, and several other micronutrients. The fats in avocados also support the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Avocados can easily be worked into your diet in a variety of ways. Mash avocado on toast, add to salads, blend into smoothies, consider a chocolate avocado “pudding” recipe, or enjoy plain for a simple way to help meet your daily magnesium needs.
Chickpeas
A half cup of cooked chickpeas provides about 40 mg of magnesium and satiating plant-based protein to support your little one’s development. The fiber content promotes digestion and regular bowel movements. Add chickpeas in soups, curries, or hummus a few times weekly for a nourishing magnesium boost.
Banana
Bananas are often known for being a good source of carbohydrates and potassium. But did you know they also contain magnesium? One medium banana packs in about 32 mg of magnesium. Add bananas to oatmeal, Greek yogurt bowls, or smoothies as a sweet way to help fulfill your daily requirements.
Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are another great source of magnesium and many other nutrients that are especially important during pregnancy. One ounce of chia seeds provides about 95 mg of magnesium.
Chia seeds are also a source of plant-based omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, non-dairy calcium, phosphorus, vitamin A, manganese, copper, zinc, non-heme iron, and potassium.

Adequate magnesium can help support a smooth pregnancy experience and reduce the risk of several complications.
Consuming adequate magnesium through magnesium-rich foods and magnesium supplementation during pregnancy provides many significant benefits for moms’ and babies’ health. Work with your healthcare provider to determine if oral magnesium supplementation is recommended to optimize your magnesium levels and reduce the risk of deficiency.
Head over to the blog to find answers to your most frequently asked preconception and pregnancy nutrition questions, such as “Is Echinacea Safe During Pregnancy?” or “Can you take magnesium while pregnant?”
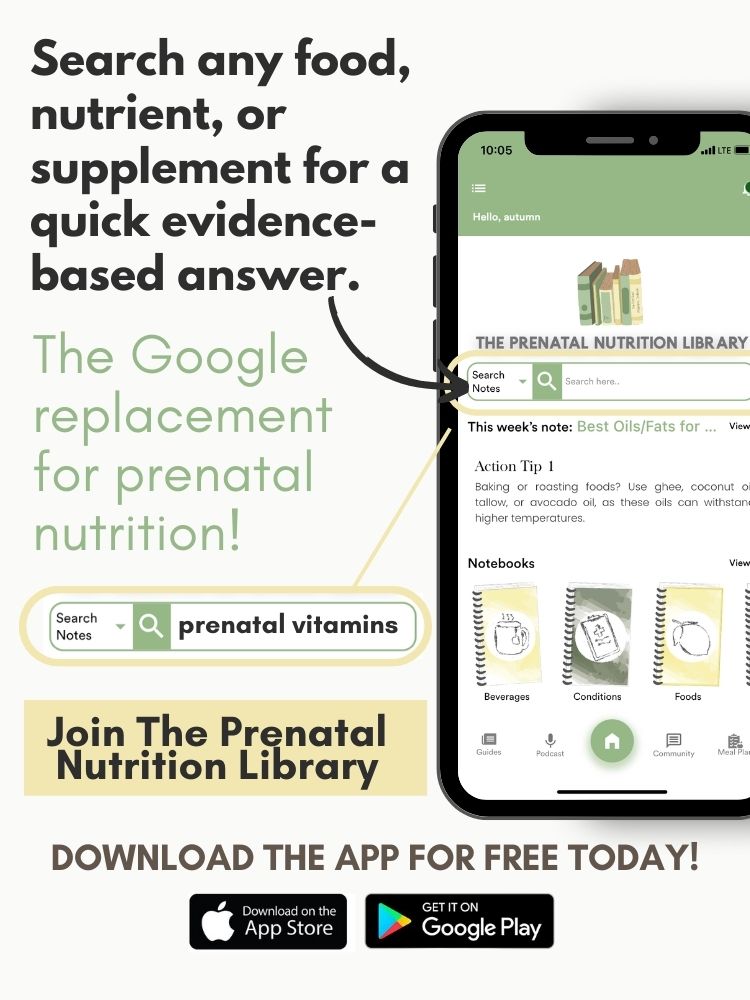
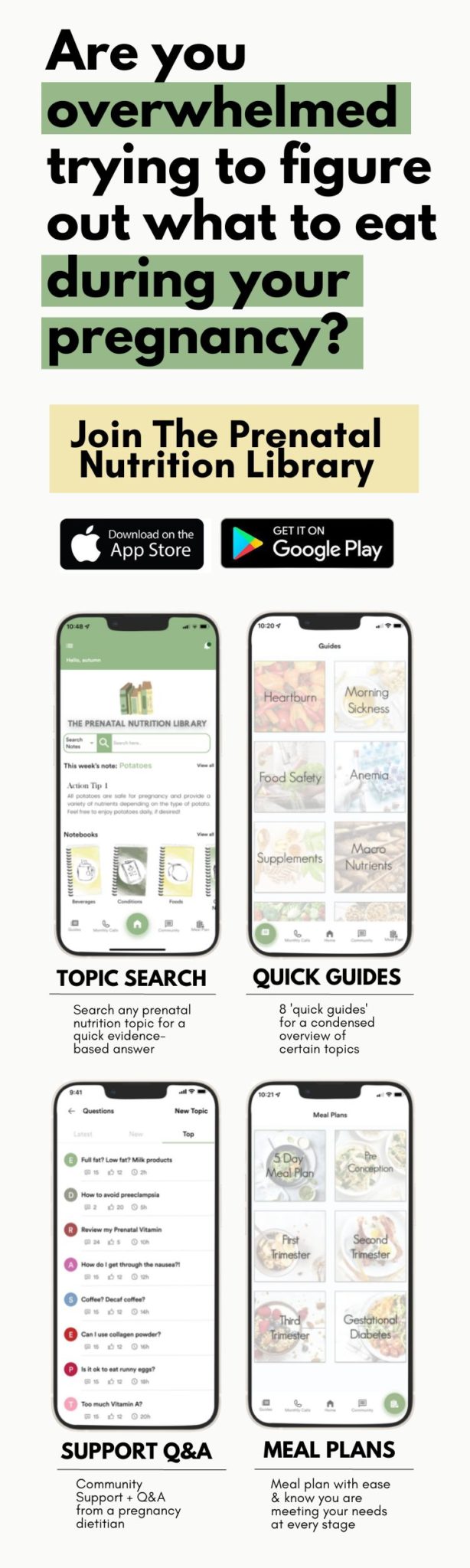
Sign up for The Prenatal Nutrition Library (TPNL) to access THOUSANDS of guides and answers to pregnancy nutrition questions. Once you sign up for TPNL, you can search through nutrients, foods, supplements, and more for a quick, evidence-based answer (at your fingertips with our App!). Sign up here!
Want to try a sample meal plan first? Grab our FREE 1-week meal plan!